The Impact Of Temperature On Germination Of Seed
Temperature plays a crucial role in seed germination, influencing both the rate and success of the process. Where growers produce their own transplants, many often experience greater success at certain times of the year than at others. These variable results are often due to the effect of temperature on germination and early plant development. Each type of seed, from the smallest herbs to large pumpkins has an optimum temperature range which is ideal for germination. Knowing where this optimal range lies for the chosen crop is vital for the consistently
successful production of seedlings.
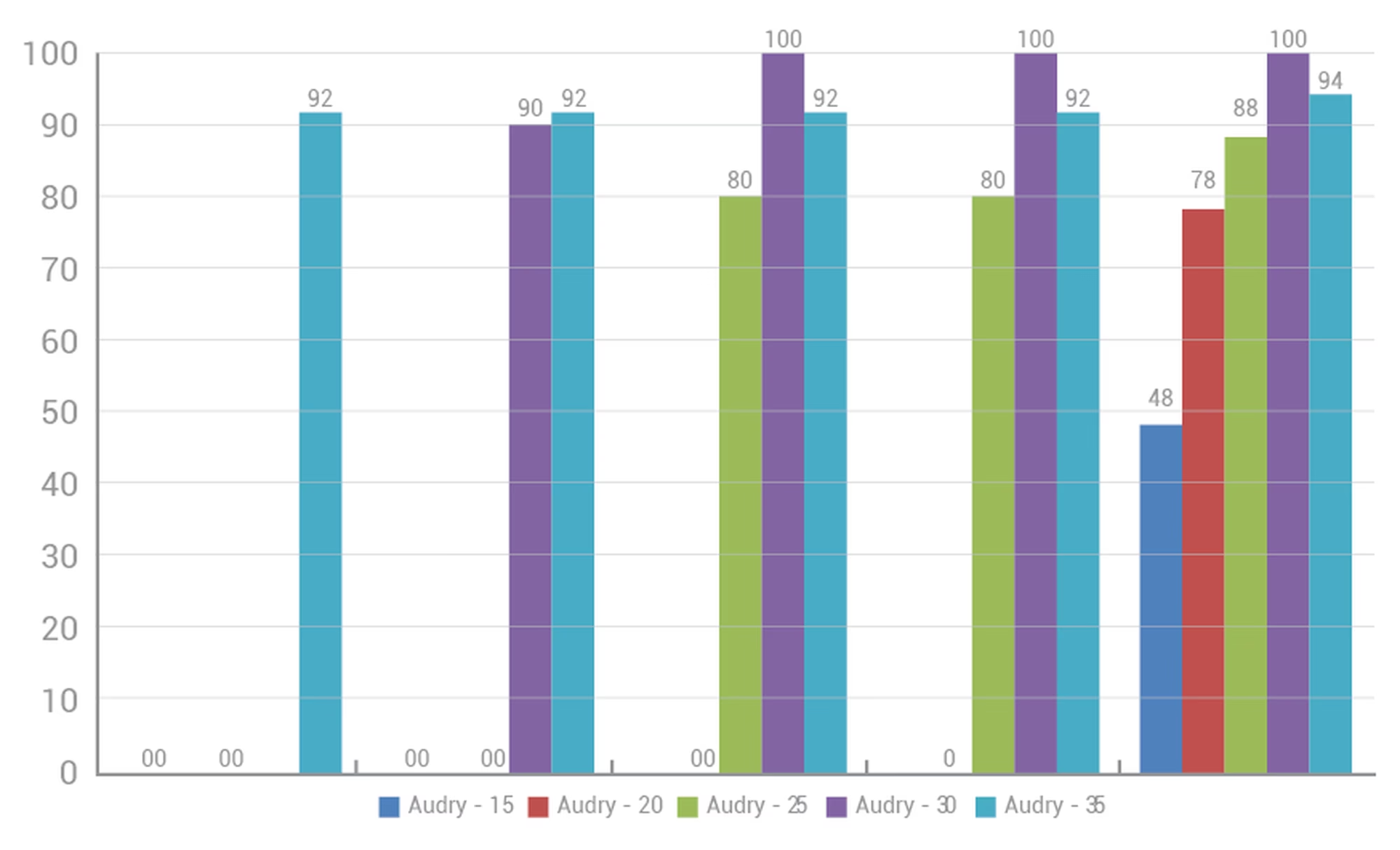
In the example below, watermelon variety Audrey was germinated at a range of temperatures between 15 and 35 ºC. Seed from the same batch number was used throughout. The only temperature that gave a 100% germination was 30ºC. A higher temperature gave quicker germination, but the final total was only 94%. This particular variety is sensitive to cooler temperatures with much slower germination and lower final counts at 25ºC and below. This gives an indication of how important temperature is in germination and the effect of cooling down seeds by regular irrigation with cold water may have.
The optimal germination temperature varies between crop types and also between varieties of the same crop. Different varieties may have different seed size and this is often an indication of a different optimal germination temperatures.

In general, larger seed is more robust and quicker to germinate under optimal conditions.

Figures 1 and 2 show seedling trays sown at the same time with the same growing medium but different varieties. The difference in development shows how varieties of the same species differ under identical conditions.
In order to grow the best possible crop, strong, uniform seedlings are required to establish the planting. Seedling production during certain times of the year is easier than in others. Where a grower is unable to control conditions under which seedlings are produced, sourcing planting material from a specialised seedling grower should be considered. Such nurseries have the experience and facilities to supply the quality and quantity of seedlings needed to give crops the best possible start.